When discussing vehicle performance and mechanics, the terms “drivetrain” and “powertrain” are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to distinct systems within a vehicle. Both systems are crucial for converting the engine’s power into movement, but understanding the differences between them is essential for proper vehicle maintenance, troubleshooting, and making informed decisions when purchasing or repairing a vehicle. In this article, we’ll break down what each term means and how they differ.
What is a Drivetrain?
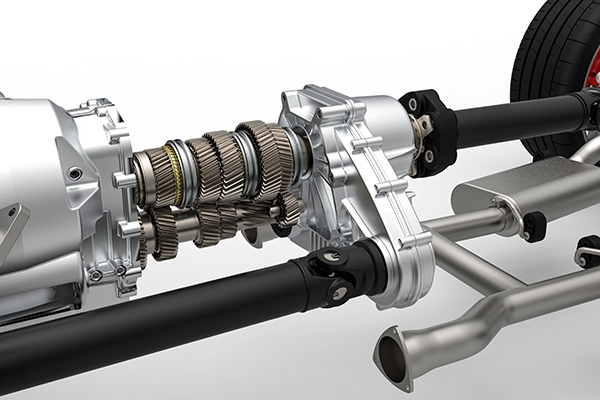
The drivetrain refers to the components that are responsible for transferring power from the transmission to the wheels. It does not include the engine but encompasses all the parts between the transmission and the wheels that allow the vehicle to move.
Key components of the drivetrain include:
- Transmission (or Gearbox): Manages the engine’s power output and adjusts the gear ratios to ensure efficient acceleration and deceleration.
- Driveshaft: Transfers power from the transmission to the differential(s).
- Differential(s): Splits the torque from the driveshaft between the wheels, allowing them to rotate at different speeds during turns.
- Axles: Deliver power from the differential to the wheels.
- CV Joints/U-Joints: Allow for the flexibility and movement of the driveshaft and axles, especially when the vehicle is turning or going over bumps.
Essentially, the drivetrain includes all the components that work to deliver engine power to the wheels, enabling movement, but does not include the engine itself.
What is a Powertrain?
The powertrain, on the other hand, refers to the entire system responsible for generating power and delivering it to the wheels. This includes not only the drivetrain but also the engine and other associated components that create and transmit power.
Key components of the powertrain include:
- Engine: The source of power in the vehicle, typically an internal combustion engine or electric motor.
- Transmission: Adjusts the engine’s output to match the desired speed and load.
- Driveshaft: Carries power from the transmission to the differential(s).
- Differential(s): Allocates power to the wheels, allowing them to rotate at different speeds when needed.
- Axles: Connect the differential to the wheels.
- Transfer Case (4WD/AWD Vehicles): Splits power between front and rear wheels in all-wheel-drive or four-wheel-drive vehicles.
- Torque Converter (Automatic Transmission Vehicles): Regulates the flow of engine power to the transmission in automatic systems.
The powertrain, therefore, includes both the engine and the drivetrain, representing the full system that is responsible for converting fuel (or electricity in the case of electric vehicles) into movement.
Drivetrain vs. Powertrain: Key Differences
- Components Included
- The drivetrain includes all the components responsible for transmitting power from the transmission to the wheels, excluding the engine.
- The powertrain includes everything from the engine to the wheels, encompassing the drivetrain as well as the engine and other power-generating components.
- Scope of Operation
- The drivetrain focuses solely on delivering the power from the transmission to the wheels. It ensures that the vehicle moves as intended, controlling how power is distributed between the wheels.
- The powertrain is a broader system that includes power generation (via the engine or motor) and the transmission of that power to the wheels. It oversees the entire process of converting fuel or electricity into motion.
- Common Issues
- Drivetrain Problems: Issues with the drivetrain typically involve components like the differential, driveshaft, or axles. Common problems include worn-out CV joints, differential failure, or a damaged driveshaft, which can lead to difficulties with turning, vibrations, or lack of power transfer to the wheels.
- Powertrain Problems: Since the powertrain includes the engine, transmission, and drivetrain, issues could involve engine problems (such as misfires, overheating, or poor fuel efficiency), transmission malfunctions (such as slipping gears or hard shifting), or any of the components in the drivetrain.
- Maintenance and Repair
- Drivetrain Maintenance: Keeping the drivetrain in top shape often requires inspecting and maintaining components like the differential, axles, and driveshaft. Regular lubrication, checking for leaks, and ensuring that the CV joints or U-joints are in good condition are key steps.
- Powertrain Maintenance: Maintaining the powertrain is a more comprehensive task, requiring regular engine maintenance (oil changes, air filter replacements, etc.), transmission servicing, and drivetrain care. Since it includes both power generation and power delivery, powertrain upkeep tends to be more complex.
Drivetrain vs. Powertrain Warranties
When purchasing a vehicle, you may encounter both drivetrain and powertrain warranties. Understanding the difference between them can help you know what parts are covered under your warranty agreement.
- Drivetrain Warranty: This type of warranty typically covers the components involved in transmitting power to the wheels, such as the transmission, driveshaft, differential, and axles. The engine is not covered under a drivetrain warranty.
- Powertrain Warranty: A powertrain warranty covers everything included in a drivetrain warranty, as well as the engine and any parts involved in generating power. This makes a powertrain warranty more comprehensive, as it protects against engine failures in addition to drivetrain issues.
Conclusion
While the drivetrain and powertrain are both essential systems in any vehicle, they refer to different sets of components. The drivetrain is focused on transmitting power to the wheels, while the powertrain encompasses the entire system, including the engine, that generates and delivers that power.
Understanding these differences can help you better maintain your vehicle, troubleshoot issues, and navigate warranties with confidence. Whether you’re driving a car, truck, or forklift, keeping both the drivetrain and powertrain in good condition is key to ensuring your vehicle operates efficiently and reliably. For more insights on drivetrain and powertrain maintenance, explore our other guides and tips!

